About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 35 results for "Renaud Bourlès" clear search
Informal risk-sharing cooperatives : ORP and Learning
Juliette Rouchier Victorien Barbet Renaud Bourlès | Published Monday, February 13, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 16, 2023The model studies the dynamics of risk-sharing cooperatives among heterogeneous farmers. Based on their knowledge on their risk exposure and the performance of the cooperative farmers choose whether or not to remain in the risk-sharing agreement.
Hedonic and Eudaimonic Well-being Based Reward for Intrinsic Motivated Reinforcement Learning Agents
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Monday, March 21, 2016The code contains four experiments for well-being based IMRL reward features.
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
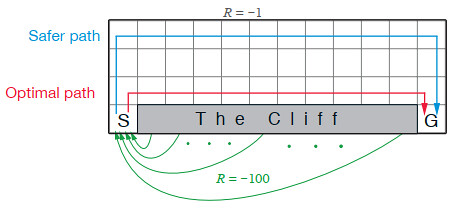
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
Spatial model of the noisy Prisoner's Dilemma with reward shift
Matus Halas | Published Thursday, March 05, 2015 | Last modified Tuesday, May 29, 2018Interactions of players embedded in a closed square lattice are determined by distance and overall gains and they lead to shifts of reward payoff between temptation and punishment. A new winner balancing against threats is ultimately discovered.
Proof of principle for a self-governing prediction and forecasting reward algorithm: Modeling consensus of a group of experts in adversarial collaboration.
Jose Osvaldo Gonzalez Hernandez Ted C. Rogers Jonathan Marino Brandon Velasco | Published Sunday, May 14, 2023Package for simulating the behavior of experts in a scientific-forecasting competition, where the outcome of experiments itself depends on expert consensus. We pay special attention to the interplay between expert bias and trust in the reward algorithm. The package allows the user to reproduce results presented in arXiv:2305.04814, as well as testing of other different scenarios.
Managing ecological disturbances: Learning and the structure of social-ecological networks
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018The aim of this model is to explore and understand the factors driving adoption of treatment strategies for ecological disturbances, considering payoff signals, learning strategies and social-ecological network structure
Equity Constrained Dispatching Model of Emergency Medical Services
Sreekanth V K Ram Babu Roy | Published Thursday, September 08, 2016 | Last modified Monday, May 01, 2017Model for evaluating various ambulance dispatching policies of an equity constrained emergency medical services under bounded rationality.
How does the world population adapt its policies on energy when it is confronted with a climate change? This model combines a climate-economy model with adaptive agents.
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
PaCE Austria Pilot Model
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, June 30, 2020The objective of building a social simulation in the Populism and Civic Engagement (PaCE) project is to study the phenomenon of populism by mapping individual level political behaviour and explain the influence of agents on, and their interdependence with the respective political parties. Voters, political parties and – to some extent – the media can be viewed as forming a complex adaptive system, in which parties compete for citizens’ votes, voters decide on which party to vote for based on their respective positions with regard to particular issues, and the media may influence the salience of issues in the public debate.
This is the first version of a model exploring voting behaviour in Austria. It focusses on modelling the interaction of voters and parties in a political landscape; the effects of the media are not yet represented. Austria was chosen as a case study because it has an established populist party (the “Freedom Party” FPO), which has even been part of the government over the years.
Displaying 10 of 35 results for "Renaud Bourlès" clear search



