About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Elena A. Pearce" clear search
Root disease model
Adam Bouche | Published Sunday, September 30, 2018This is a model of root disease spread between trees in the landscape. The disease spreads via two transmission processes: (a) root contact/root graft transmission between adjacent trees and (b) insect vectors that carry spores between trees. Full details can be found in the “Info” tab in the model and in the readme file in the GitHub repository.
COVID-19 ABM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, April 21, 2020Model of the Corona pandemic outbreak
The COVID-19 ABM aims to predict the qualitative behaviour of the CoViD-19 epidemic dynamics for the greater region of Salzburg City. Specifically, by means of scenario testing, it aims to help assessing how containment interventions can allow a stepwise relaxation of the lockdown without risking a new outbreak.
How does the world population adapt its policies on energy when it is confronted with a climate change? This model combines a climate-economy model with adaptive agents.
An agent-based model of scapegoating
Carlos Paes | Published Thursday, August 28, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, August 28, 2025This agent-based model investigates scapegoating as a social mechanism of crisis management. Inspired by René Girard’s mimetic theory, it simulates how individual tension accumulates and spreads across a small-world network. When tension exceeds certain thresholds, leaders emerge and accuse marginalized agents, who may attempt to transfer blame to substitutes. If scapegoating occurs, collective tension decreases, but victims become isolated while leaders consolidate temporary authority. This simulation provides a conceptual and methodological framework for exploring how collective blame, crisis contagion, and leadership paradoxes emerge in complex networks. It can also be extended with empirical data, such as social media dynamics of online harassment and virtual lynching, offering potential applications for both theoretical research and practical crisis monitoring.
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
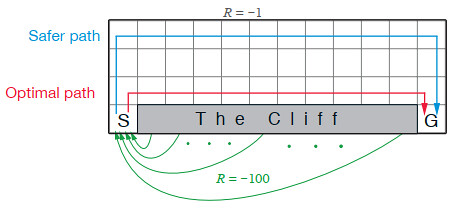
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
ABM Simulation of Transition from Late Longshan Cultures to Early Erlitou Culture
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Within the archeological record for Bronze Age Chinese culture, there continues to be a gap in our understanding of the sudden rise of the Erlitou State from the previous late Longshan chiefdoms. In order to examine this period, I developed and used an agent-based model (ABM) to explore possible socio-politically relevant hypotheses for the gap between the demise of the late Longshan cultures and rise of the first state level society in East Asia. I tested land use strategy making and collective action in response to drought and flooding scenarios, the two plausible environmental hazards at that time. The model results show cases of emergent behavior where an increase in social complexity could have been experienced if a catastrophic event occurred while the population was sufficiently prepared for a different catastrophe, suggesting a plausible lead for future research into determining the life of the time period.
The ABM published here was originally developed in 2016 and its results published in the Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference.
SMILI-T: Small-scale fisheries institutions and local interactions for transformations
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Tuesday, January 09, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 26, 2021This model examines how financial and social top-down interventions interplay with the internal self-organizing dynamics of a fishing community. The aim is to transform from hierarchical fishbuyer-fisher relationship into fishing cooperatives.
Peer reviewed MHMSLeptoDy (Multi-host, multi-serovar Leptospira Dynamics Model)
Aniruddha Belsare Matthew Gompper Meghan Mason Claudia Munoz-Zanzi | Published Tuesday, January 29, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, March 12, 2019Leptospirosis is a neglected, bacterial zoonosis with worldwide distribution, primarily a disease of poverty. More than 200 pathogenic serovars of Leptospira bacteria exist, and a variety of species may act as reservoirs for these serovars. Human infection is the result of direct or indirect contact with Leptospira bacteria in the urine of infected animal hosts, primarily livestock, dogs, and rodents. There is increasing evidence that dogs and dog-adapted serovar Canicola play an important role in the burden of leptospirosis in humans in marginalized urban communities. What is needed is a more thorough understanding of the transmission dynamics of Leptospira in these marginalized urban communities, specifically the relative importance of dogs and rodents in the transmission of Leptospira to humans. This understanding will be vital for identifying meaningful intervention strategies.
One of the main objectives of MHMSLeptoDy is to elucidate transmission dynamics of host-adapted Leptospira strains in multi-host system. The model can also be used to evaluate alternate interventions aimed at reducing human infection risk in small-scale communities like urban slums.
Generic servicising model (SPREE project)
Igor Nikolic Reinier Van Der Veen Kasper H Kisjes | Published Wednesday, August 26, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, September 28, 2016This generic agent-based model allows the user to simulate and explore the influence of servicising policies on the uptake of servicising and on economic, environmental and social effects, notably absolute decoupling.
04 TpLab V2.08 – Teleological Pruning Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Our societal belief systems are pruned by evolution, informing our unsustainable economies. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Elena A. Pearce" clear search






